Why Membrane Bioreactor is the Future of Wastewater Treatment in Industries
Recognizing Membrane Bioreactors: The Future of Wastewater Treatment
Membrane layer bioreactors (MBRs) stand for a noteworthy technology in the field of wastewater treatment, incorporating organic processes with sophisticated membrane layer filtration to boost effluent quality. As worldwide water deficiency and stringent regulative structures become progressively pushing concerns, MBR technology uses a reliable response with its capacity to minimize footprint and enhance source recuperation.
What Are Membrane Bioreactors?
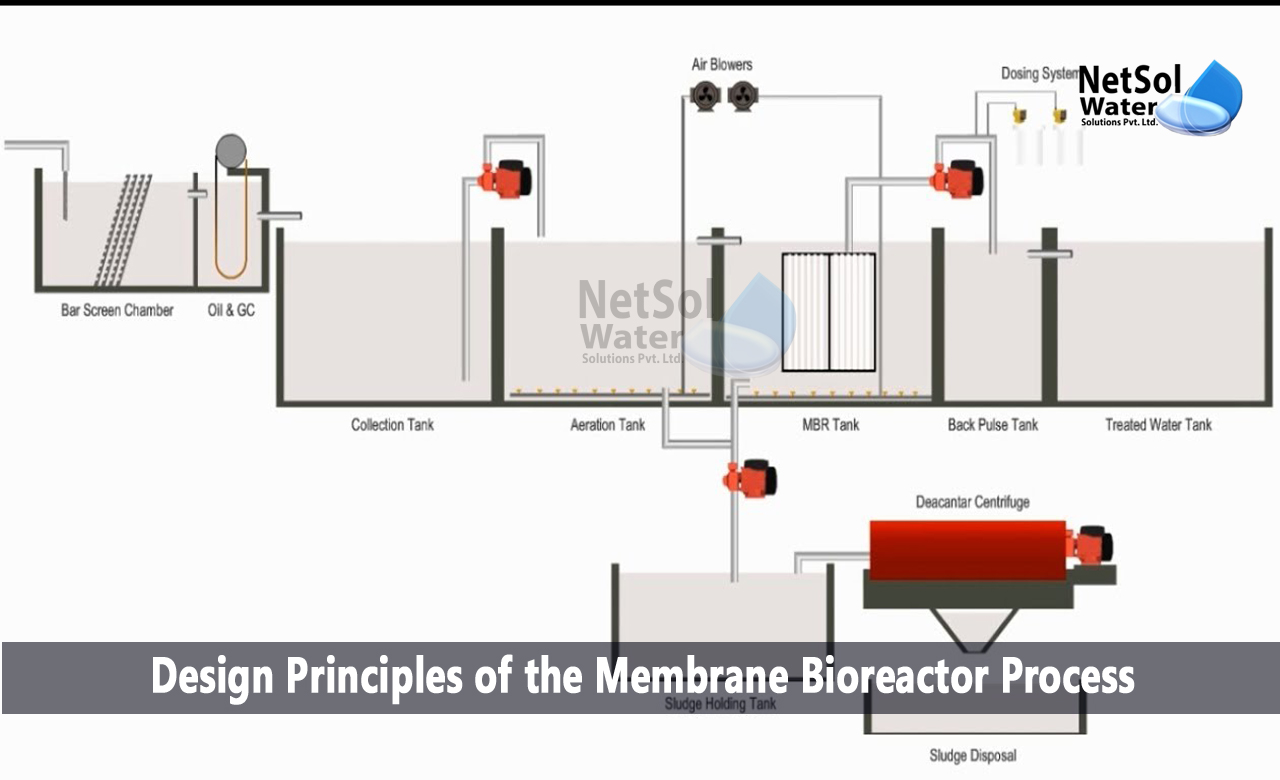
The core components of MBR systems consist of a bioreactor where microbial activity happens and a membrane layer device that filterings system the combined alcohol. This double performance allows the simultaneous degradation of organic issue and solid-liquid splitting up in a solitary step. MBRs can operate in both submerged and external configurations, with submerged systems being more common due to their compact design and functional performance.
The fostering of MBR modern technology has actually obtained grip in different applications, varying from local wastewater treatment to industrial effluent management. MBRs are particularly advantageous in scenarios where room is rigid or restricted effluent high quality standards must be fulfilled. By keeping a high focus of bacteria within the bioreactor, MBRs enhance the degradation of natural contaminants, thus yielding greater therapy effectiveness compared to typical approaches.
Trick Benefits of MBR Technology
The combination of biological therapy with membrane purification in MBR systems provides countless advantages that establish it besides traditional wastewater therapy methods. Among the primary benefits is the boosted effluent high quality. MBRs properly eliminate put on hold solids and microorganisms, achieving greater degrees of purification that fulfill stringent discharge requirements and facilitate water reuse applications.
One more considerable benefit is the reduced sludge production. MBR systems produce much less excess sludge, leading to lower disposal expenses and a decline in ecological impact. The closed nature of the membrane system lessens the threat of smell emissions and enhances general procedure control.
Last But Not Least, MBRs are versatile and adaptable, making them appropriate for different wastewater kinds, consisting of commercial and municipal sources. The ability to integrate with sophisticated treatment innovations additionally boosts their performance, making MBRs an encouraging remedy for the future of wastewater management.
Challenges and Limitations of MBRs
While MBR technology offers numerous advantages, it also faces several challenges and constraints that can influence its prevalent fostering. One substantial difficulty is the high funding and operational costs connected with MBR systems. The initial financial investment for membrane layer products you could look here and the required infrastructure can be substantial, making it much less easily accessible for smaller industries or districts.
In addition, membrane layer fouling remains a crucial concern that can lessen system efficiency and increase upkeep needs. Fouling occurs when solids, organic issue, or bacteria accumulate on the membrane layer surface, leading to lowered leaks in the structure and calling for regular cleaning or substitute.
An additional restriction entails the complexity of the innovation. MBR systems require proficient workers for procedure and upkeep, which can be a barrier in regions with minimal technological proficiency. Moreover, the disposal of spent membranes presents ecological issues, as the products are frequently check my blog not naturally degradable and can add to throw away monitoring difficulties.
Last But Not Least, while MBRs can effectively deal with a vast array of wastewater, they may not be suitable for all applications, especially those with high focus of fats, oils, and oils, necessitating additional research study and technology to address these limitations.
Applications of Membrane Bioreactors
In different markets, membrane bioreactors (MBRs) have become a versatile service for wastewater therapy (Membrane Bioreactor). Their applications extend community, commercial, and farming settings, showcasing their adaptability and efficiency in diverse atmospheres. In local wastewater treatment plants, read the full info here MBRs substantially enhance effluent high quality, enabling water reuse and reducing the ecological influence of discharged wastewater
Industrially, MBRs are utilized in food and drink processing, fabric production, and pharmaceutical manufacturing, where they effectively deal with high-strength waste streams. Their ability to deal with rising and fall tons and differing impurity focus makes them specifically valuable in these sectors. Furthermore, MBRs assist in the removal of pathogens, suspended solids, and natural matter, adding to conformity with strict discharge regulations.
In farming, MBRs are increasingly utilized for dealing with agricultural drainage and livestock wastewater, enabling the healing of nutrients for fertilizer manufacturing. They also help in the therapy of greywater for watering, advertising sustainable water administration techniques.
The adaptability of MBRs is additional confirmed by their assimilation with various other technologies, such as anaerobic digestion and progressed oxidation processes, enhancing overall performance and resource recovery in wastewater treatment systems.
The Future of Wastewater Treatment
Improvements in technology and an expanding focus on sustainability are forming the future of wastewater therapy. Membrane bioreactors (MBRs) exhibit this shift by integrating biological treatment processes with membrane filtering, causing top quality effluent suitable for reuse. The trend in the direction of circular economic situations is triggering centers to embrace MBRs for their capability to recoup resources, such as water and nutrients, from wastewater.
Advancements in membrane products and setup are boosting the effectiveness and durability of MBR systems, lowering functional prices and energy consumption. Smart technology combination, including real-time monitoring and automated control systems, is additional maximizing efficiency and making it possible for anticipating maintenance, thus lessening downtime.
In addition, regulative stress and social assumptions are pushing industries and communities to take on more lasting methods. Membrane Bioreactor. The change towards decentralized wastewater treatment options is acquiring grip, permitting for local treatment that decreases transport costs and power usage
Verdict
Membrane layer bioreactors (MBRs) stand for a transformative method to wastewater treatment, incorporating organic processes with sophisticated membrane technology. The benefits of MBRs, including boosted effluent top quality, reduced spatial demands, and lower sludge production, place them as a feasible option amidst expanding urbanization and more stringent ecological policies. In spite of existing difficulties, the continued development in membrane layer materials and functional approaches assures to boost the efficiency and adoption of MBRs, guaranteeing their essential role in the future of lasting wastewater management.
Membrane bioreactors (MBRs) represent a noteworthy development in the field of wastewater treatment, incorporating biological procedures with innovative membrane purification to boost effluent quality.Membrane bioreactors (MBRs) integrate organic treatment processes with membrane filtration to efficiently deal with wastewater.The combination of organic therapy with membrane layer purification in MBR systems uses many advantages that establish it apart from typical wastewater therapy methods. Membrane layer bioreactors (MBRs) exemplify this change by incorporating organic treatment procedures with membrane filtering, resulting in top notch effluent appropriate for reuse.Membrane bioreactors (MBRs) represent a transformative approach to wastewater therapy, integrating organic processes with innovative membrane layer modern technology.